As a system administrator you might want to use either MBR or GPT while partitioning. Let's explore some basic concepts about MBR and GPT, thier advantages, limitations and differences.
What is the use of GPT and MBR ?
Master Boot Record (MBR) and GUID Partition Table (GPT) are two distinct ways of storing the partition information on a drive. This information includes where partition begin and start, so the operating system know which sector belongs to each partition and which is bootable. This is the reason you need to choose between MBR and GPT, before creating partitions on a hard drive.
Master Boot Record
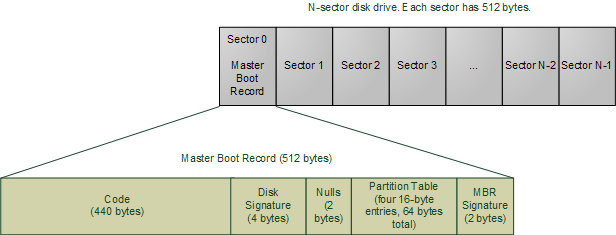
Master Boot Record (MBR) disk use the standard BIOS partition table. It is the information in the first sector of any hard disk that identifies how and where the operating system is located so that it can be loaded into the main memory of the system. This sector contains the boot loader for the installed operating system and information about the drive's logical partition. The master boot record is also sometimes called as "partition sector" or "master partition table" because it includes table that locates each partition tht the hard disk is been formatted into. MBR works with disks upto 2 TB in size. It also supports only 4 primary partitions, if you want more partitions than you have to create one of your primary partition into "extended partition" and further creates logical partitions inside it.
GUID Partition Table
Globally Unified Identifier Partition Table or GPT is a new standard acting as a replacement of MBR. GPT use Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). It’s called GUID Partition Table because every partition on your drive has a “globally unique identifier,” or GUID that is a random string so long that every GPT partition on earth likely has its own unique identifier. One advantage of GPT disk is that you can have more than 4 partitions on each disks. GPT allows nearly about unlimited amount of partitions depending upon your operating system. GPT is also required for disks larger than 2 terabytes.Using GPT a drive could support between 8 and 9.4 ZB depending on the sector size. On an MBR disk, the partitioning and boot data is stored in one place. If this data is overwritten or corrupted, the whole system might get corrupted. Whereas, GPT stores multiple copies of this data across the disk, so it’s much more robust and can recover if the data is corrupted.
What is the use of GPT and MBR ?
Master Boot Record (MBR) and GUID Partition Table (GPT) are two distinct ways of storing the partition information on a drive. This information includes where partition begin and start, so the operating system know which sector belongs to each partition and which is bootable. This is the reason you need to choose between MBR and GPT, before creating partitions on a hard drive.
Master Boot Record
Master Boot Record (MBR) disk use the standard BIOS partition table. It is the information in the first sector of any hard disk that identifies how and where the operating system is located so that it can be loaded into the main memory of the system. This sector contains the boot loader for the installed operating system and information about the drive's logical partition. The master boot record is also sometimes called as "partition sector" or "master partition table" because it includes table that locates each partition tht the hard disk is been formatted into. MBR works with disks upto 2 TB in size. It also supports only 4 primary partitions, if you want more partitions than you have to create one of your primary partition into "extended partition" and further creates logical partitions inside it.
GUID Partition Table
Globally Unified Identifier Partition Table or GPT is a new standard acting as a replacement of MBR. GPT use Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). It’s called GUID Partition Table because every partition on your drive has a “globally unique identifier,” or GUID that is a random string so long that every GPT partition on earth likely has its own unique identifier. One advantage of GPT disk is that you can have more than 4 partitions on each disks. GPT allows nearly about unlimited amount of partitions depending upon your operating system. GPT is also required for disks larger than 2 terabytes.Using GPT a drive could support between 8 and 9.4 ZB depending on the sector size. On an MBR disk, the partitioning and boot data is stored in one place. If this data is overwritten or corrupted, the whole system might get corrupted. Whereas, GPT stores multiple copies of this data across the disk, so it’s much more robust and can recover if the data is corrupted.

Thank you for the insight!
ReplyDelete